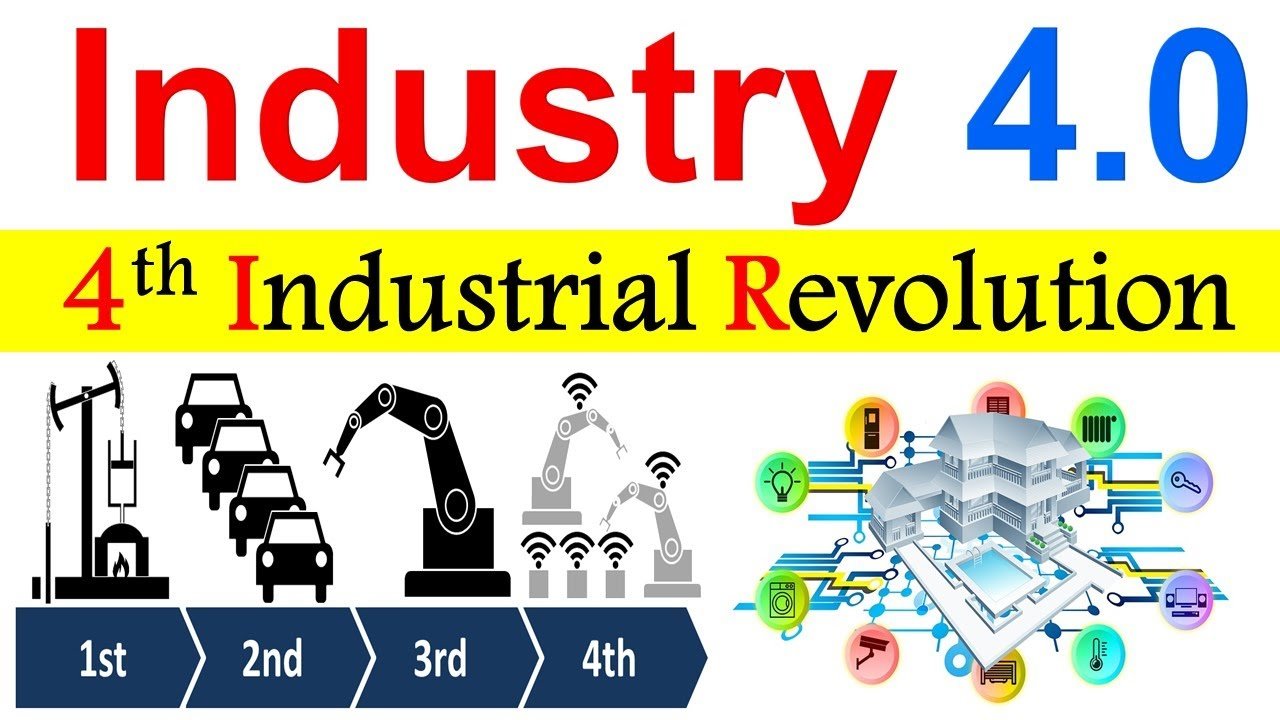
The concept of Industry 4.0, also known as the Fourth Industrial Revolution, is transforming the landscape of manufacturing and industrial processes.

This revolution leverages cutting-edge technologies to create smart factories, increase efficiency, and drive innovation across various sectors.
In this comprehensive article, we will delve into what Industry 4.0 is, its components, benefits, challenges, and its impact on different industries.
Understanding Industry 4.0
Definition of Industry 4.0
Industry 4.0 refers to the current trend of automation and data exchange in manufacturing technologies.
It encompasses cyber-physical systems, the Internet of Things (IoT), cloud computing, and cognitive computing.
Essentially, it’s the smart integration of these technologies to create a more connected, efficient, and adaptable production environment.
The Evolution of Industrial Revolutions
First Industrial Revolution
The First Industrial Revolution began in the late 18th century and was marked by the transition from manual production methods to machine-based manufacturing.
It introduced water and steam power, significantly boosting productivity.
Second Industrial Revolution
The Second Industrial Revolution occurred in the late 19th and early 20th centuries.
This era was characterized by mass production, electrification, and the introduction of assembly lines, further enhancing manufacturing capabilities.
Third Industrial Revolution
The Third Industrial Revolution, also known as the Digital Revolution, started in the mid-20th century.
It brought about the advent of computers, digital systems, and automation, paving the way for significant advancements in information technology.
Key Components of Industry 4.0
Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS)
Cyber-Physical Systems integrate computation, networking, and physical processes.
In Industry 4.0, CPS connects and controls the physical world through software systems, enhancing automation and enabling real-time decision-making.
Internet of Things (IoT)
IoT involves connecting physical devices to the internet, allowing them to collect and exchange data.
In manufacturing, IoT devices monitor equipment performance, track inventory, and optimize processes, contributing to greater efficiency and reduced downtime.
Big Data and Analytics
Big Data refers to the vast volumes of data generated by modern manufacturing processes.
Analytics tools process this data to provide actionable insights, helping companies make informed decisions and predict future trends.
Cloud Computing
Cloud computing enables the storage, management, and processing of data over the internet.
It provides scalable resources, facilitates collaboration, and reduces the need for on-premises infrastructure.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning
AI and machine learning algorithms analyze data and identify patterns, enabling predictive maintenance, quality control, and process optimization.
These technologies enhance decision-making and drive innovation in manufacturing.
Autonomous Robots
Autonomous robots operate independently and can perform complex tasks with minimal human intervention.
In smart factories, these robots work alongside humans to increase productivity and reduce errors.
Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR)
AR and VR technologies provide immersive experiences for training, maintenance, and design.
They enable workers to visualize complex data and processes, improving efficiency and accuracy.
Benefits of Industry 4.0
Increased Efficiency and Productivity
Industry 4.0 technologies streamline production processes, reduce downtime, and optimize resource utilization.
This leads to higher efficiency, increased output, and lower operational costs.
Enhanced Quality Control
Advanced sensors and analytics ensure real-time monitoring and control of production processes.
This results in higher product quality, reduced defects, and improved customer satisfaction.
Greater Flexibility and Customization
Smart factories can quickly adapt to changes in demand and customize products to meet specific customer requirements.
This flexibility enhances competitiveness and opens new market opportunities.
Improved Supply Chain Management
IoT and big data analytics provide end-to-end visibility of the supply chain.
This enables better inventory management, demand forecasting, and logistics optimization, reducing lead times and costs.
Better Decision Making
Data-driven insights empower managers to make informed decisions.
Predictive analytics helps anticipate problems before they occur, enabling proactive measures and minimizing disruptions.
Challenges of Industry 4.0
Data Security and Privacy
The integration of connected devices increases the risk of cyberattacks and data breaches.
Ensuring robust cybersecurity measures and protecting sensitive information is crucial.
High Implementation Costs
Adopting Industry 4.0 technologies requires significant investment in infrastructure, training, and system integration.
Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) may face financial barriers to implementation.
Workforce Adaptation
The shift to automated and data-driven processes demands a workforce with new skills.
Upskilling and reskilling employees is essential to bridge the gap and ensure a smooth transition.
Interoperability Issues
Integrating diverse systems and technologies can be challenging.
Ensuring seamless communication and compatibility between different components is vital for effective implementation.
Industry 4.0 in Different Sectors
Manufacturing
Smart Factories
Smart factories leverage IoT, AI, and robotics to create interconnected production environments.
They enable real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and optimized workflows, resulting in higher efficiency and reduced costs.
Additive Manufacturing
Additive manufacturing, or 3D printing, allows the production of complex and customized parts with minimal waste. This technology is revolutionizing prototyping and small-scale production.
Healthcare
Personalized Medicine
Industry 4.0 technologies enable the analysis of vast amounts of medical data, facilitating personalized treatment plans.
IoT devices monitor patient health in real-time, improving outcomes and reducing hospital visits.
Smart Medical Devices
Smart medical devices, such as wearable sensors and connected implants, provide continuous monitoring and remote diagnostics.
This enhances patient care and supports preventive healthcare initiatives.
Agriculture
Precision Farming
IoT and big data analytics enable precision farming, where sensors monitor soil conditions, crop health, and weather patterns.
This data-driven approach optimizes resource use, increases yields, and reduces environmental impact.
Autonomous Farming Equipment
Autonomous tractors, drones, and robotic harvesters automate labor-intensive tasks, increasing efficiency and productivity in agriculture.
Transportation and Logistics
Connected Vehicles
Connected vehicles use IoT technology to communicate with each other and infrastructure, enhancing traffic management and safety.
This reduces congestion, fuel consumption, and emissions.
Smart Warehousing
IoT-enabled warehousing systems optimize inventory management, track goods in real-time, and streamline logistics operations.
This results in faster order fulfillment and lower operational costs.
The Future of Industry 4.0
Continued Technological Advancements
The future of Industry 4.0 will be marked by further advancements in AI, machine learning, and IoT.
These technologies will continue to evolve, driving greater automation and innovation across industries.
Increased Collaboration
Collaboration between industries, academia, and governments will be crucial for the successful implementation of Industry 4.0.
Joint efforts will address challenges, promote standardization, and foster innovation.
Sustainable Manufacturing
Sustainability will be a key focus of Industry 4.0. Technologies that reduce waste, optimize resource use, and minimize environmental impact will become increasingly important.
Conclusion
Industry 4.0 represents a significant leap forward in the evolution of industrial processes.
By integrating advanced technologies such as IoT, AI, and cyber-physical systems, it creates smarter, more efficient, and adaptable manufacturing environments.
While the benefits are substantial, the challenges of data security, high implementation costs, workforce adaptation, and interoperability must be addressed.
As we move forward, continued advancements and collaborations will shape the future of Industry 4.0, driving innovation and sustainability across various sectors.